
|
|
Abstract: Electron-microscope enlarged structures that appear to form Bahá'í symbols. From "Basal Body and Flagellar Development during the Vegetative Cell Cycle and the Sexual cycle of Chlamydomonas Reinhardii." Notes: Scan of entire issue by J. Gunasekaran (1999); high-res images scanned by Graham Ashford (2006). This entire issue can be downloaded as a PDF (2.9MB). |
Nine-pointed star in microscopic images of the algae Chlamydomonas
by T. Cavalier-Smith
published in Journal of Cell Science, 16:3, page 552Cambridge University Press, 1974-12
1. About
 Axoneme, at Wikipedia |
For more information on this algae, see the Chlamydomonas Genetics Center.
A similar image appears in the book What is Life? by Lynn Margulis and Dorion Sagan (2000), with the following description:
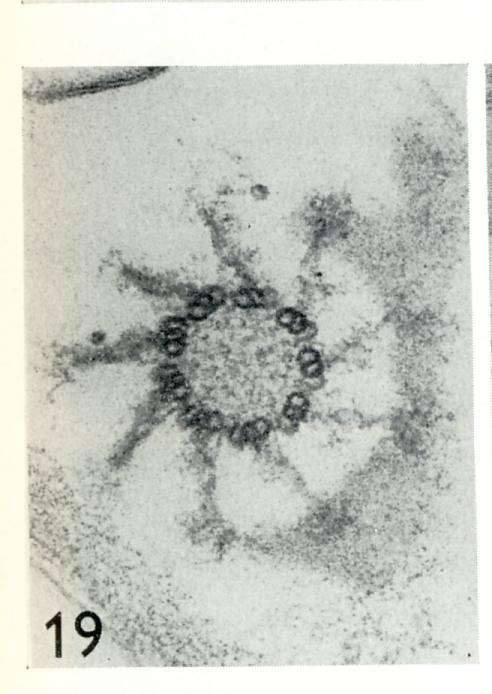
Undulipodium in cross section. The shaft (axoneme) displays the 9(2)+2 arrangement of microtubules. This distinct intracellular organization is found in the sperm cells of widely diverse beings throughout the natural world, from men to ginkgo trees. Electron micrographs of cuts through the shafts of the cilia propelling swimming paramecia and trichomonads and the cilia that push the egg through a woman's fallopian tube also reveal this 9(2)+2 pattern.Rather than being unique to Chlamydomonas reinhardii, this pattern may be very common in nature. See similar pictures at wikipedia.org/wiki/Axoneme. [addition by John Bremberek, 2014-04]
2. For comparison: 9-pointed star, and Bahá'í Ringstone Symbol (for comparison of the letter ha)

3. Various pages from the Journal of Cell Science
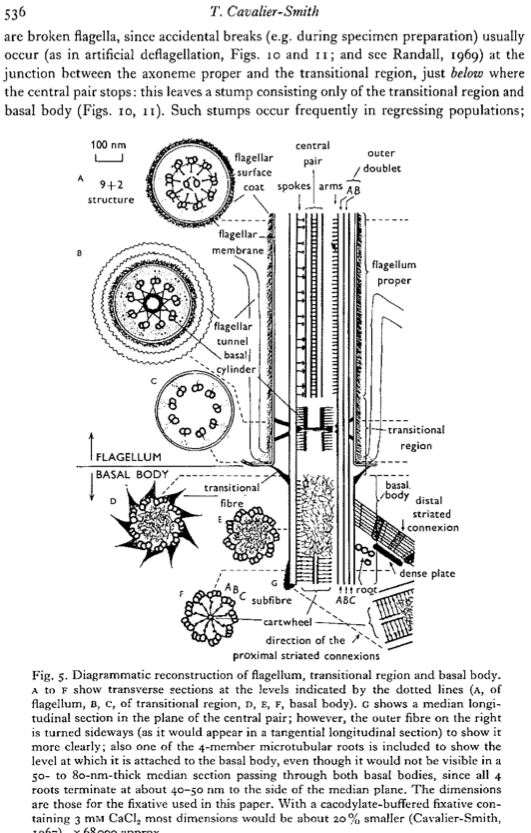 Figure 5: click for larger image |
 page 549: click for larger image |
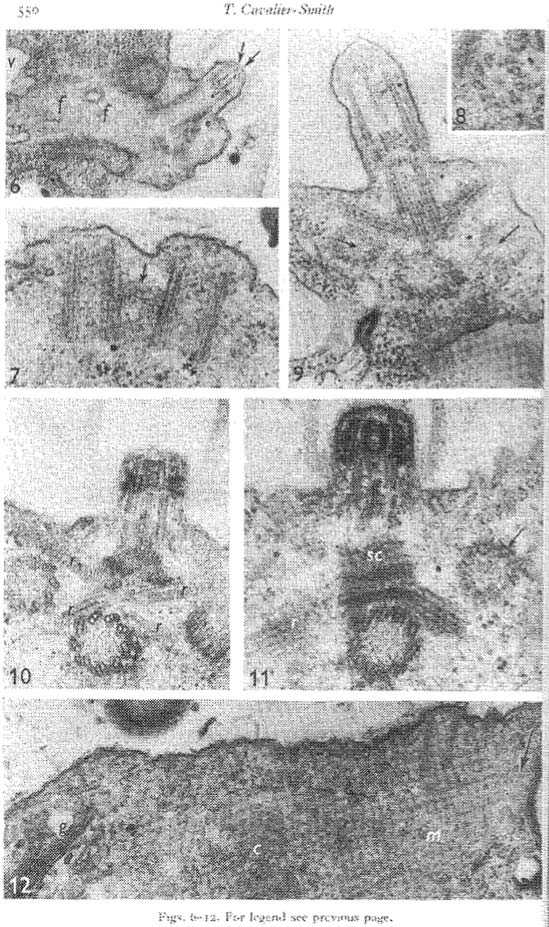 Figure 10: click for larger image |
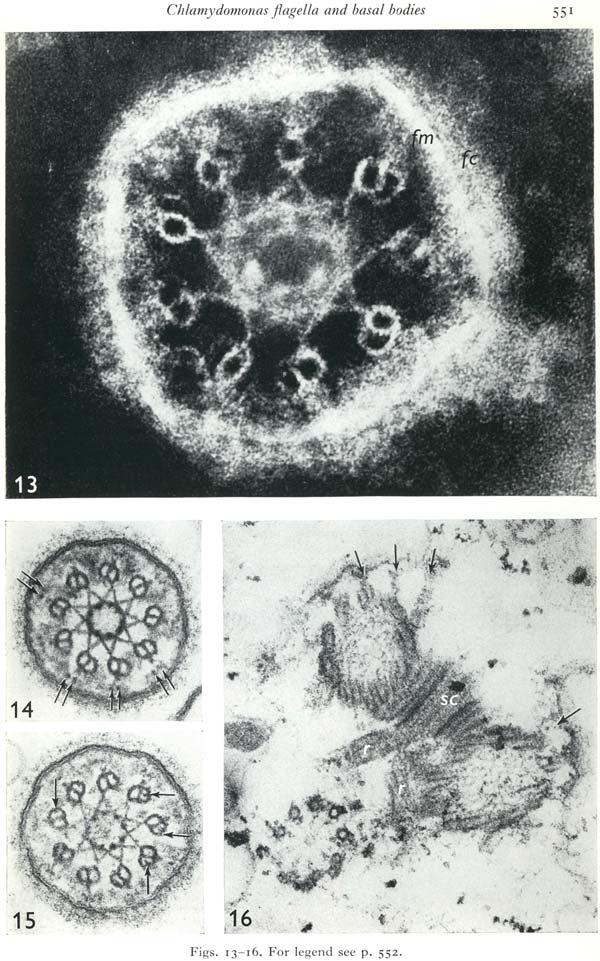 page 551: click for larger image |
 page 552: click for larger image |
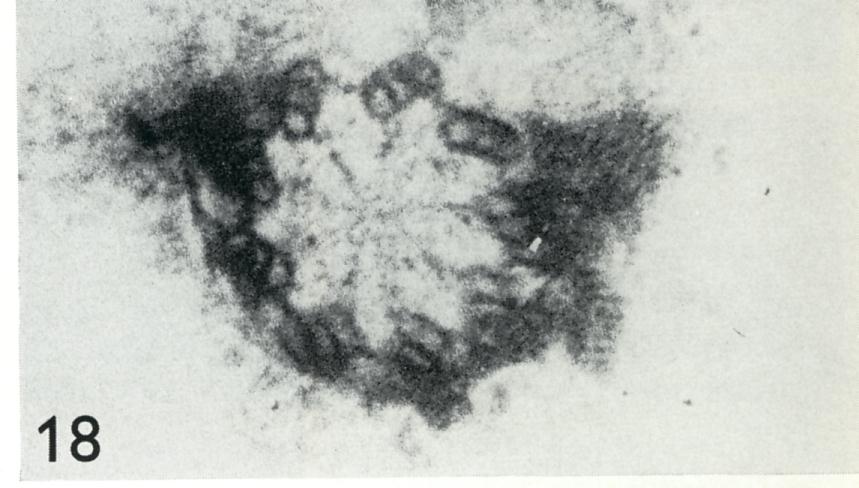
- Figs. 13-16. Chlamydomonas transitional regions and basal bodies from cell
homogenates.
Fig. 13. Negatively stained transitional region lying flat on the grid, showing fiagellar surface coat (fc), flagellar membrane (fin) and the globular substructure of the outer doublets, and of the star pattern surrounding the basal cylinder. x 320000.
Fig. 14. Transverse section through the distal part of the transitional region. That part of the annular connexion lying between the outer doublets and the membrane is not homogeneous but contains densities placed in pairs (arrows) opposite each doublet outer projection. x 120000.
Fig. 15. Transverse section through the proximal part of the transitional region's basal cylinder. Doublet outer projections and paired densities are present, and Btubules knobs can be seen clearly in places (arrows). The flagellar surface coat is very well preserved. x 120000.
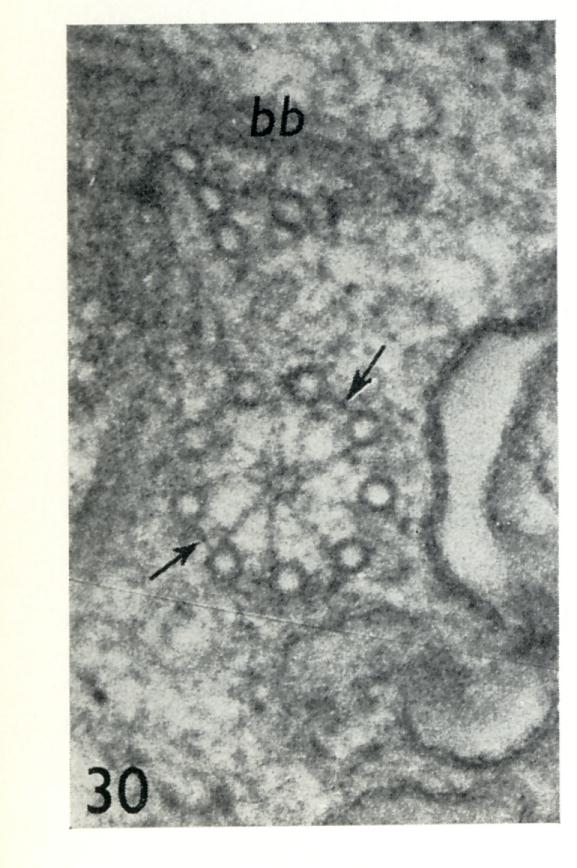
Fig. 16. Two mature triplet basal bodies still joined to each other by the distal striated connexion (sc) and to the plasma membrane fragments by transitional fibres (arrows). A developing basal body consisting of a cartwheel plus 6 singlets and 3 triplets is connected to the mature basal body pair by amorphous material that appears to be attached to fragments of the microtubular roots (r). x 120000.
|
|